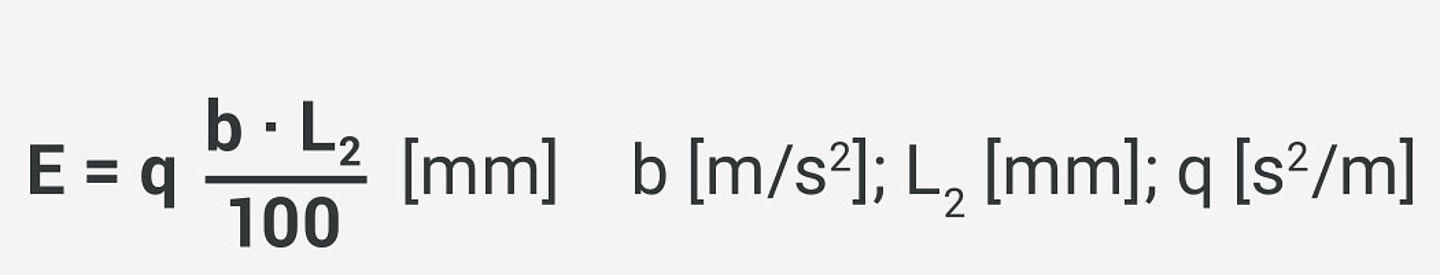Gear Metering Pumps & Meter Mix Dispense Machines with highest accuracy for processing liquids and pastes.
High-precision rotary stroke bearings for backlash-free linear and rotational movements for use in machine and device construction.







Ball-bearing guides for linear and rotational movements without play for use in all technical areas where reliability and precision are required.

The guide diameter finely honed to ISO tolerance IT 3 guarantees the preload of the ball bearing guide in combination with shaft diameter ISO-h3.
Universal, slim inner bevels on both sides.

Permanently installed thrust washers on both sides provide a safe travel limit for the ball cage.

Permanently installed thrust washers on each side and sealing rings prevent impurities from getting into the ball bearing guide.

Extra sturdy model with scrapers on both sides which reliably prevent impurities from getting in, even in very dirty environments.

Universal, slim inner bevels on both sides, for use with ball cage from mini series N502.
Permanently installed thrust washers on both sides provide a safe travel limit for the ball cage from mini series N502.
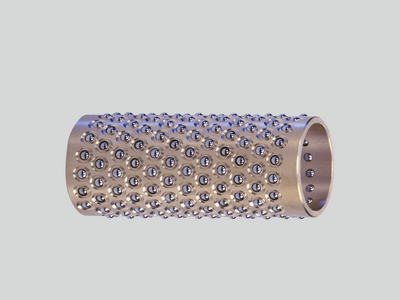
The balls can move easily without getting lost. The balls are arranged in such a way that they run smoothly and ensure a long service life of the ball bearing guide.

Excellent dry run properties and maximum smoothness, even at high accelerations thanks to the lightweight plastic.

Versatile with balls arranged along a helical line, ideal for linear movements and rotational movements.

Smaller balls used with same shaft diameter compared to type N501. Reduced installation space thanks to guide bushes from the mini series.

High loading capacity thanks to large number of balls, reliable travel limit for the cage thanks to the securing ring.

The finely-ground surface is ideal for high precision ball bearing guides, ensuring smooth running and a long service life of the ball bearing guide.
Preload is guaranteed when using with Mahr guide bushes and ball cages.

Inner thread on both sides, preload is guaranteed when using with Mahr guide bushes and ball cages.

Broader and more optimized range of uses.

Protect open ball-bearing guides against dirt without compromising smooth movement.

Lubrication for maximum performance and corrosion prevention.
Permissible accelerations during linear movement
High inertia forces can occur on the ball cage during fast linear movements. During movements that are similar to sinusoidal motions, the mass forces are the highest in the end positions of the linear motion.
The magnitude of the inertia forces is influenced by the following factors:
- Cage material: brass or plastic
- Longitudinal acceleration b
- Cage length L2
- Horizontal or vertical installation position
The required ball contact length E is calculated using the quotient q based on the relationship:
Acceleration b with sinusoidal motion:
The quotient q is specified in the following tables.
The calculated value for E [mm] must be compared with the recommendations in the table. The larger of the two values is used to determine the size of the bearing. The tables contain recommended values for the permissible longitudinal acceleration with ball cage being inside the guide bush at its entire length. These values are average values that can be exceeded, for example, by increasing the preload v.